Director
Dr. Soroush is founder and director of TDNA engineering consultancy with more than 12 years of research, teaching and industrial experience in transportation and traffic engineering, transportation planning and public transportation. He has a deep understanding of traffic engineering’s principle alongside with extensive knowledge and experience of data mining, machine learning and statistical analysis. Through his knowledge and managerial experience, he has successfully delivered variety of complex traffic engineering projects. He is an active member of Auckland University’s Transportation Research Centre and results from his own PhD in application of machine learning to estimate bus travel time and dwell time in Auckland have been published in several prestigious journals and awarded for excellence. Membership of local and international bodies ensures he remains up to date with the latest transportation research techniques and outcomes and underpins his provision of high-quality project delivery to clients in line with best practice.
Why We Are The Best
We are traffic engineers and data scientists who have spent considerable time on traffic and transport assessments for evidence based decision making using different data sources.
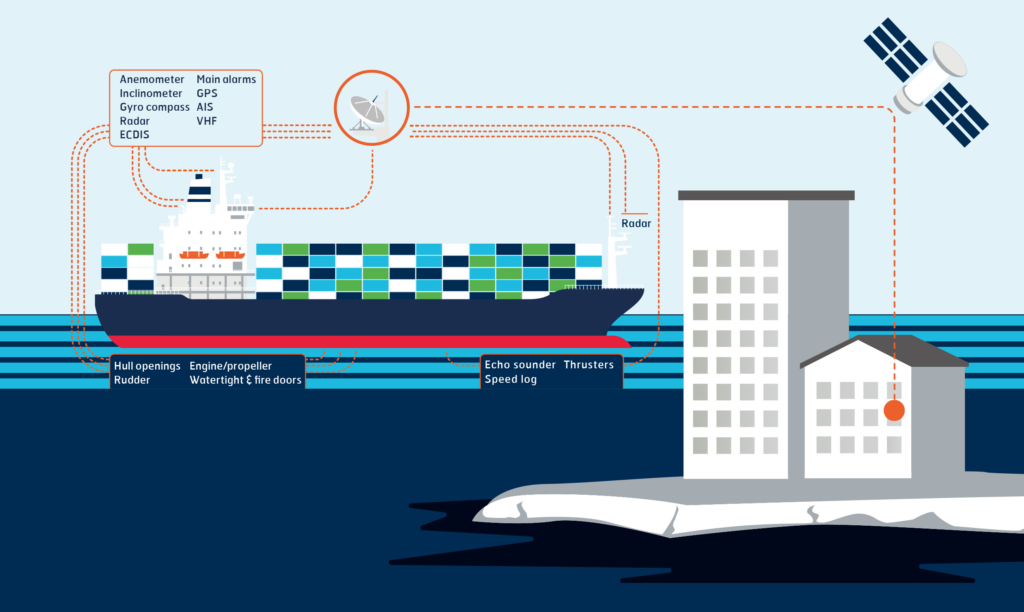
Fleet Data

GPS Data
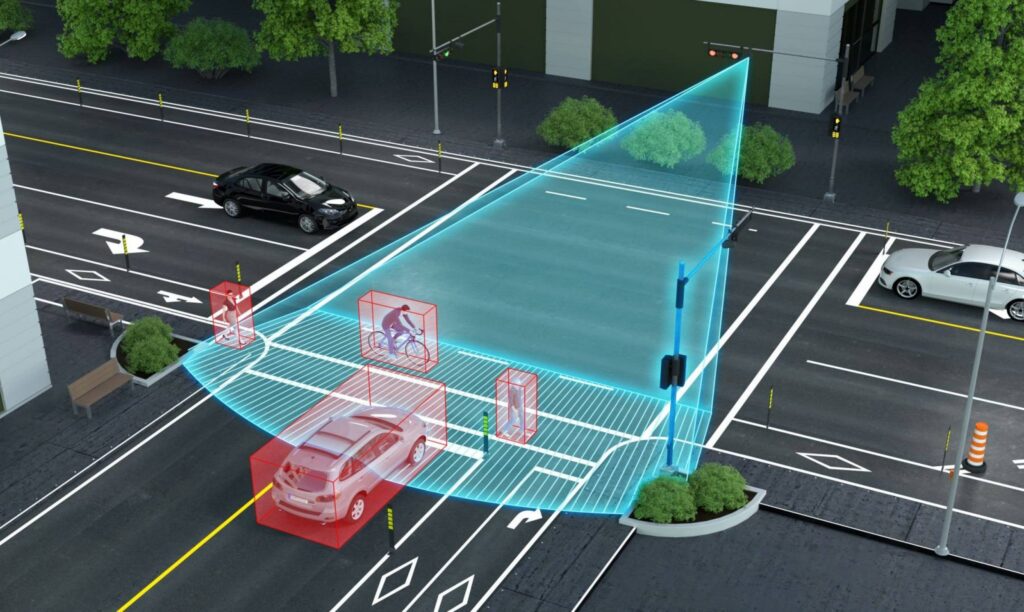
Traffic Volume-SCATS Data
Travel Time - Speed Data

Video-Image Data

Text Data

Loop Detector Data

Crash Data

Transport Asset Data
- Bluetooth Data
- Probe Data
- Geographic Information System
- Weather Data
- Public Transport Data
- Population Data
- Behavioural insights
- Weigh-in-motion Data
- CellPhone Data
- Autroads
- Monetised Benefits and Costs Manual
- Highway Capacity Manual

Bluetooth is an open wireless technology standard for transmitting fixed and mobile electronic device data over short distances. Bluetooth was introduced in 1994 as a wireless substitute for RS-232 cables.
Bluetooth communicates with a variety of electronic devices and creates personal networks operating within the unlicensed 2.4 GHz band. Operating range is based on device class. A variety of digital devices use Bluetooth, including MP3 players, mobile and peripheral devices and personal computers.
Bluetooth technology has been widely recognized as an effective, low-cost traffic data source in freeway traffic contexts. Bluetooth technology can provide travel time (TT) information in complex urban traffic environments.

Probe data is defined as data that is generated by monitoring the position of individual vehicles (i.e., probes) over space and time rather than measuring characteristics of vehicles or groups of vehicles at a specific place and time.
Work zones present problems when it comes to performance measures since, by definition, they are not fixed in space or time. This reduces the value of data generated by traditional fixed sensors – fixed sensors may not be located where needed to monitor work zone traffic or may be out of service because of work zone activities.
Probe data provides an alternate means of obtaining data on work zone traffic conditions to support work zone performance
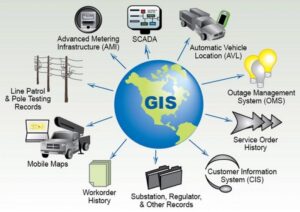
A geographic information system (GIS) is a system that creates, manages, analyzes, and maps all types of data. GIS connects data to a map, integrating location data (where things are) with all types of descriptive information (what things are like there). This provides a foundation for mapping and analysis that is used in science and transport industry.
GIS helps users understand patterns, relationships, and geographic context. The benefits include improved communication and efficiency as well as better management and decision making.

Weather can be defined as the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place. It can be hot, cold, wet, or dry. Weather is always changing, and it is affected by many factors, such as air pressure, temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation.
Weather affects the operation of the transportation systems that we all rely on—from vehicles slowed by a wet surface to delivery trucks delayed by high winds. Gathering weather data is key to have reliable traffic and transport models and predictions.

Public transportation systems include a variety of transit options such as buses, light rail, and subways. Public transportation contributes to a healthier environment by improving air quality and reducing oil consumption, and through better land-use policies. It also helps to expand business development and work opportunities. And, it is critical for emergency situations requiring safe and efficient evacuation.
As stated in Public Transport 2045 the main message “is that public transport needs to be at the core of a shared mobility future. Otherwise, we risk facing higher levels of motorized traffic and congestion in our cities.”
New Zealand national population estimates give the best measure between census dates of the population that usually lives in an area, by age and sex, for the total New Zealand area.
Population is on of the most important influential factor in traffic and transportation engineering. Majority of management as well as engineering operations are done on the basis of population changes.

While new technological developments, new infrastructure and expanded mobility options are aiding to curb congestion, the biggest factor in improving urban travel actually relies upon a completely different factor: "human behaviour".
“Providing more choices in line with our personal situations is key to changing behavior. People’s preferred travel choices aren’t always best for their communities. It’s time to think beyond transportation silos and present alternative options to create a better, more seamless travel experience - Conduent Survey .”

Weigh-in-motion (WiM) systems are still a fairly young technology. Like many developing technology platforms, these are subject to fragmentation in terms of uses and standard. In New Zealand WiM data is collected at six locations on the state highway network which provides useful information on the characteristic of the New Zealand heavy vehicle fleet.
![]()
The explosive growth in the availability of mobile phones in societies around the world – even in some of the poorest, most remote communities – is increasingly leading many groups Data input or captured into phones may be transmitted or shared in many ways (including SMS, MMS, USSD, Bluetooth, wireless Internet, or the exchange of physical memory cards). Where mobile connectivity is not available, data can be stored on the phone and transmitted later once a phone is within sufficient range of a cell tower. These data can be used as a complement source to provide transport engineers and practitioners valuable speed, travel time and origin destination data.

Austroads as a collective of the Australian and New Zealand transport agencies provides high-quality, practical and impartial advice, information, tools and services to help the members to deliver efficient, reliable and safe mobility to the customers.
Austroads solves problems for transport agencies in Australia and New Zealand with the focus on making mobility safer and more reliable for all users . It also provide national services that help transport agencies to operate seamlessly across state borders and bring national efficiencies to their operations

Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency's Monetised benefits and costs manual (MBCM) is the industry's standard for the economic evaluation of land transport activities in New Zealand. The MBCM sets out economic evaluation procedures and values used in calculating benefit–cost ratios, necessary for applications seeking investment where a cost–benefit appraisal is a mandatory Waka Kotahi requirement.
The MBCM has replaced the Economic evaluation manual from 31 August 2020 and applies to business cases that commence on or after 31 August 2020.

The Highway Capacity Manual (HCM) is a publication of the Transportation Research Board (TRB) in the United States. It contains concepts, guidelines, and computational procedures for computing the capacity and quality of service of various highway facilities, including freeways, highways, arterial roads, roundabouts, signalized and unsignalized intersections, interchanges, rural highways, and the effects of mass transit, pedestrians, and bicycles on the performance of these systems. HCM is widely used around the world as one of the standard transportation engineering codes.